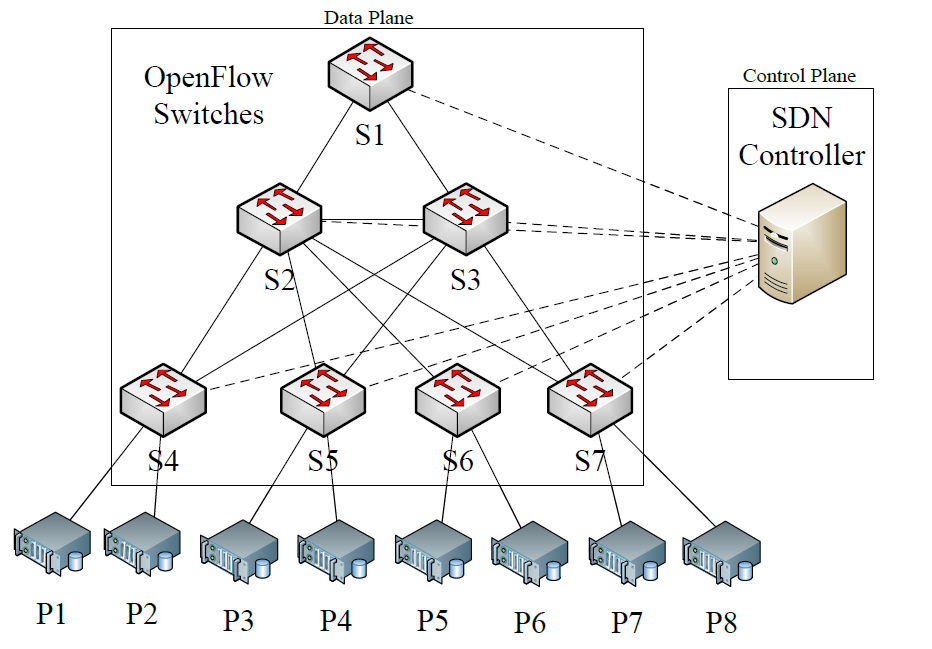
Transmission of data in intelligent smart grids (SG) is definitely dependent on the communication infrastructure of the network and how it communicates. The data transfer that connects to the AMI in the infrastructure brings together data from smart meters for analysis and management to a data centre. In general, the data centre is storing data. Note that, with the expansion of SG, fundamental mechanisms have lost their significance, thus posing difficulties, such as data centre overload. Therefore, there is a vital need for the softwarization of SG. To this end, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is quite handy. With SDN and the aid of software-based controllers alongside predesigned APIs (e.g. OpenFlow protocol), an entire network and its elements may be controlled and programmed as a unified network. Software-centric data centres (SDDCs) are a new generation of information bays that work more on virtualization and software-centric technologies, and are less reliant on hardware or physical infrastructure layers. The main objective of this paper is to implement a software-centric data centre (SDN) for the smart grid. In this regard, the proposed architectures of data centres are based on the concepts of SDN and placed in a real test environment, implemented and evaluated under different factors and scenarios. The evaluation results are also discussed in depth.